Wi-Fi has become an essential part of our daily lives, enabling us to connect to the internet without physical cables. From homes and offices to coffee shops and airports, wireless networking provides seamless connectivity for our devices. But how does Wi-Fi actually work?
In this guide, we’ll explore the fundamentals of wireless networking, including Wi-Fi standards, security protocols, and common troubleshooting techniques.
🔍 What is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) is a technology that uses radio waves to transmit data between devices and a network. It allows laptops, smartphones, tablets, and other devices to connect to the internet without a physical wired connection.
Wi-Fi operates using radio frequencies (RF) in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, and newer generations also support 6 GHz for faster speeds and reduced congestion.
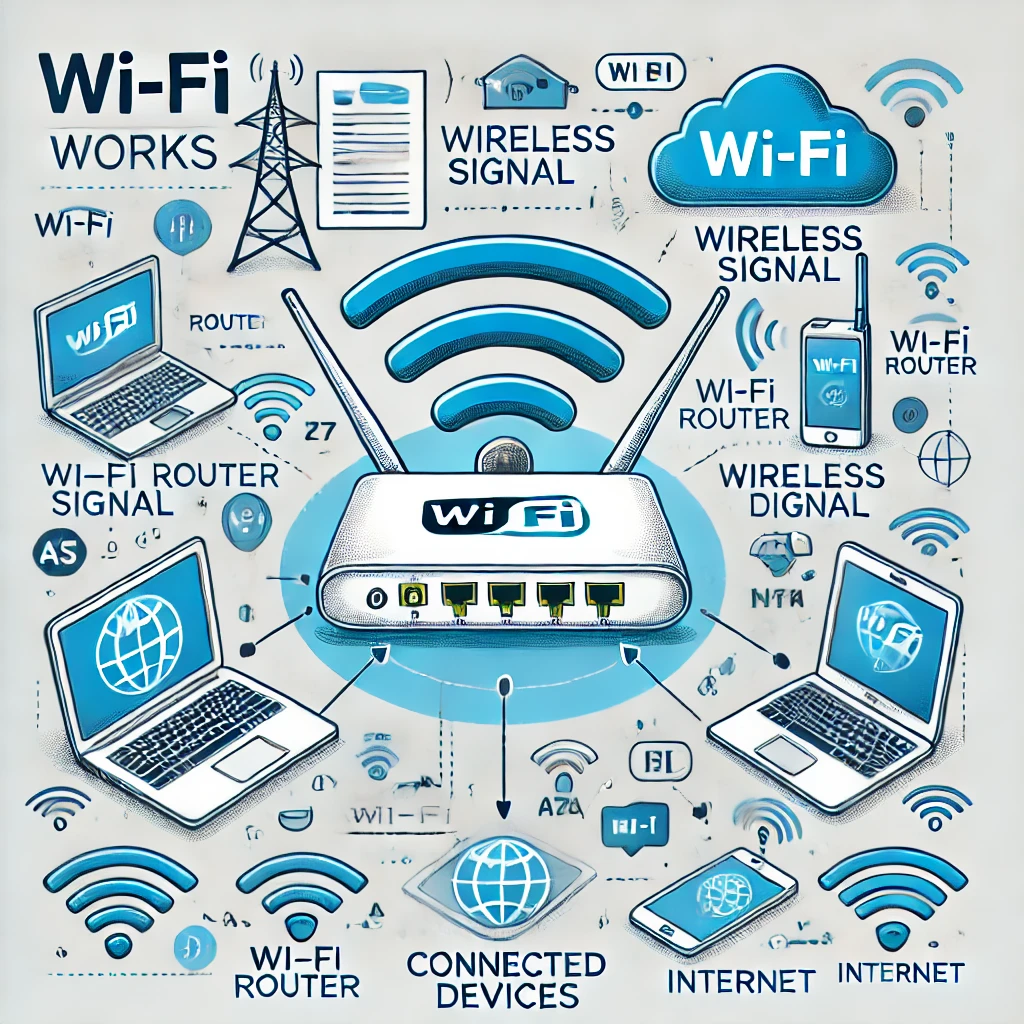
⚙️ How Does Wi-Fi Work?
1️⃣ A router or access point (AP) sends wireless signals using radio waves.
2️⃣ A Wi-Fi-enabled device (laptop, phone, etc.) detects the signal and connects to the network.
3️⃣ The router acts as a bridge between the wireless devices and the internet, forwarding data to and from the ISP (Internet Service Provider).
📡 Wi-Fi Standards: Understanding Different Generations
Wi-Fi technology has evolved over time, with different standards improving speed, range, and efficiency.
| Wi-Fi Standard | Speed (Max) | Frequency | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n) | 600 Mbps | 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz | MIMO (Multiple antennas) |
| Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) | 3.5 Gbps | 5 GHz | Beamforming, MU-MIMO |
| Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) | 9.6 Gbps | 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz | Higher efficiency, OFDMA |
| Wi-Fi 6E | 9.6 Gbps | 6 GHz | Less interference, low latency |
| Wi-Fi 7 (Upcoming) | 30 Gbps+ | 2.4, 5, & 6 GHz | Higher capacity, improved performance |
Which Wi-Fi standard should you use?
- Wi-Fi 6 or 6E is the best for faster speeds, multiple devices, and high-performance applications like gaming and video streaming.
- Wi-Fi 5 is still widely used and offers good performance.
- Wi-Fi 4 is mostly found in older devices and is slower compared to newer standards.
🔐 Wi-Fi Security Protocols: Keeping Your Network Safe
Wi-Fi networks need encryption and authentication to prevent unauthorized access and hacking attempts.
| Security Protocol | Description | Security Level |
|---|---|---|
| WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) | Outdated & easily hacked | ❌ Weak |
| WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) | Improved security over WEP | ⚠️ Moderate |
| WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2) | Industry standard for security | ✅ Strong |
| WPA3 | Latest and most secure protocol | 🔒 Very Strong |
Best Security Practices:
✅ Use WPA2 or WPA3 encryption to protect your network.
✅ Change the default SSID (Wi-Fi network name) and password.
✅ Enable MAC address filtering to limit which devices can connect.
✅ Disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) to prevent brute-force attacks.
✅ Use a strong, unique Wi-Fi password with at least 12+ characters.
⚡ Common Wi-Fi Problems and Troubleshooting
Even the best Wi-Fi networks can face connectivity issues. Here are some common problems and how to fix them.
1️⃣ Slow Wi-Fi Speeds
🔹 Cause: Interference, too many connected devices, outdated equipment.
🔹 Solution:
- Move closer to the router.
- Use a wired Ethernet connection for high-speed tasks.
- Upgrade to a Wi-Fi 6 or 6E router.
- Reduce interference by changing Wi-Fi channels.
2️⃣ Wi-Fi Keeps Disconnecting
🔹 Cause: Weak signal, router firmware issues, or ISP problems.
🔹 Solution:
- Restart your router and modem.
- Update router firmware.
- Ensure your device drivers are up to date.
3️⃣ Devices Can’t Connect to Wi-Fi
🔹 Cause: Incorrect password, MAC filtering, or security settings.
🔹 Solution:
- Check the Wi-Fi password and re-enter it.
- Disable MAC address filtering and test again.
- Reset network settings on your device.
4️⃣ Dead Spots in Your Home
🔹 Cause: Large homes, walls, and obstacles blocking Wi-Fi signals.
🔹 Solution:
- Use Wi-Fi extenders or mesh systems for better coverage.
- Place the router in a central location and elevate it.
🔮 Future of Wi-Fi: What’s Next?
The future of Wi-Fi looks promising with upcoming Wi-Fi 7, which will offer even faster speeds, lower latency, and improved connectivity for smart homes, gaming, and enterprise applications.
As 5G and Wi-Fi continue to evolve, they will complement each other to provide seamless, high-speed wireless experiences.
🎯 Final Thoughts
Wi-Fi has transformed the way we connect to the internet, offering convenience, flexibility, and high-speed access to online services. Understanding how Wi-Fi works, upgrading to the right standard, and applying best security practices will help you get the most out of your wireless network.
Need more networking tips? Follow Packet-Switched.com for expert insights on wireless technologies and IT best practices! 🚀

Wireless networking has revolutionized the way we connect to the internet, providing seamless communication and convenience. *Wireless Networking: How Wi-Fi Works* explores the fundamentals of Wi-Fi technology, explaining how data is transmitted wirelessly and the factors that influence network performance. Understanding these concepts helps users optimize their connections for better speed, security, and reliability. As technology continues to evolve, Wi-Fi remains a crucial part of modern connectivity, shaping the way we work, communicate, and access information.